The Future of Space Exploration
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, our blue planet has embarked on a journey of discovery, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and technological prowess. At the forefront of this cosmic odyssey is the red planet, Mars. Recent missions to Mars have captured the imagination of people worldwide, marking significant milestones in our space exploration endeavors. These missions have not only provided invaluable insights into the Martian landscape and atmosphere but have also raised intriguing questions about the possibility of life beyond Earth.
But Mars is not the final frontier. As we stand on the cusp of new discoveries, we must ask ourselves: What lies beyond Mars? What secrets do the distant stars, galaxies, and unknown realms of space hold? As we set our sights on deeper space exploration, we are not just seeking answers to scientific questions. We are on a quest to understand our place in the vast universe. The journey to Mars is just one chapter in humanity’s ongoing story of exploration. And as we turn the page, the next chapters promise even greater adventures and revelations.
A Glimpse into NASA’s Vision
NASA, the beacon of space exploration, has always been driven by a vision that extends far beyond the confines of our planet. Rooted in a commitment to human exploration, technology, and science. NASA’s endeavors have consistently pushed the boundaries of what’s possible, transforming the unknown realms of space into domains of human knowledge and achievement.
Central to this vision is the belief that our journey in space is not a series of isolated missions, but a continuum of exploration. While Mars has been a focal point in recent years, NASA’s eyes have always been set on horizons further afield. Recognizing the challenges of deep space exploration, NASA has strategically envisioned the Moon as more than just a celestial neighbor. The Moon, with its proximity and resources, is seen as a crucial stepping stone. A testing ground for technologies, strategies, and missions that will be vital for journeys to Mars and beyond.
The plan to return to the Moon is not just about revisiting old footsteps. It’s about establishing a sustainable human presence. Building infrastructures, and fostering collaborations that will serve as a springboard for future deep space missions. By harnessing the Moon’s potential, NASA aims to pave the way for humanity’s next giant leaps in space. Ensuring that our voyage to the stars is not just a dream, but a tangible, achievable reality.
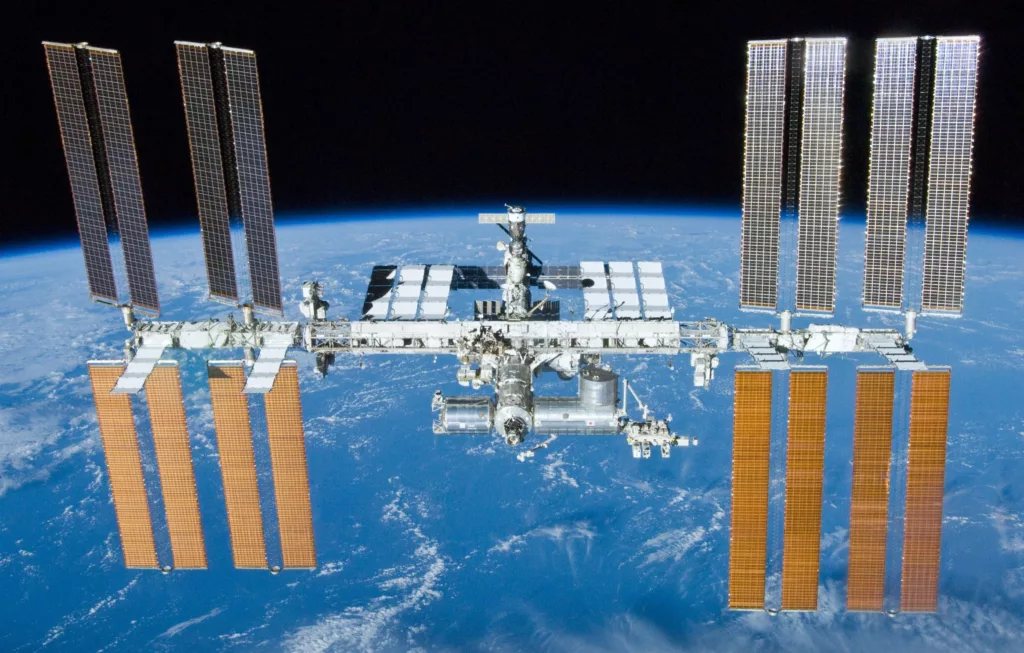
The Role of Commercial and International Partnerships
The landscape of space exploration has undergone a transformative shift in recent decades. Gone are the days when nations raced against each other, vying for supremacy in the cosmos. Today, the narrative is one of collaboration. Where countries and companies come together, pooling resources, expertise, and vision to achieve common goals in space.
This shift from competition to collaboration signifies a recognition that the challenges and opportunities of space exploration are too vast for any single entity to tackle alone. International partnerships, such as the International Space Station (ISS) collaboration, exemplify how nations can achieve more together than they ever could individually. These alliances not only foster technological and scientific advancements but also promote peace, understanding, and shared aspirations among nations.
Parallel to international collaborations, the rise of commercial companies in the space sector has been nothing short of revolutionary. Companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic are no longer just contractors. They are pioneers, innovators, and visionaries in their own right. Their endeavors, from launching reusable rockets to conceptualizing space tourism, are reshaping the economics and possibilities of space travel. By introducing cost-effective technologies, innovative designs, and ambitious missions, these commercial entities are accelerating the pace of space exploration and democratizing access to the cosmos.
Furthermore, the synergy between governmental space agencies and commercial companies is paving the way for a new era in space exploration. Through partnerships, contracts, and collaborative missions, they are jointly building the infrastructure, technologies. And platforms that will define the future of humanity’s presence in space.
In essence, the future of space exploration is a tapestry woven from threads of international cooperation and commercial innovation. Together, they promise a future where the wonders of the cosmos are not just the domain of a few, but a shared journey for all of humanity.
The Next Big Destinations: Moon and Beyond
As we chart the course of future space exploration, our celestial neighbor, the Moon, emerges as a pivotal destination. But this isn’t a mere redux of the Apollo missions. The focus now is on regions of the Moon previously unexplored and on establishing a sustainable presence that can serve as a launchpad for missions farther into the cosmos.
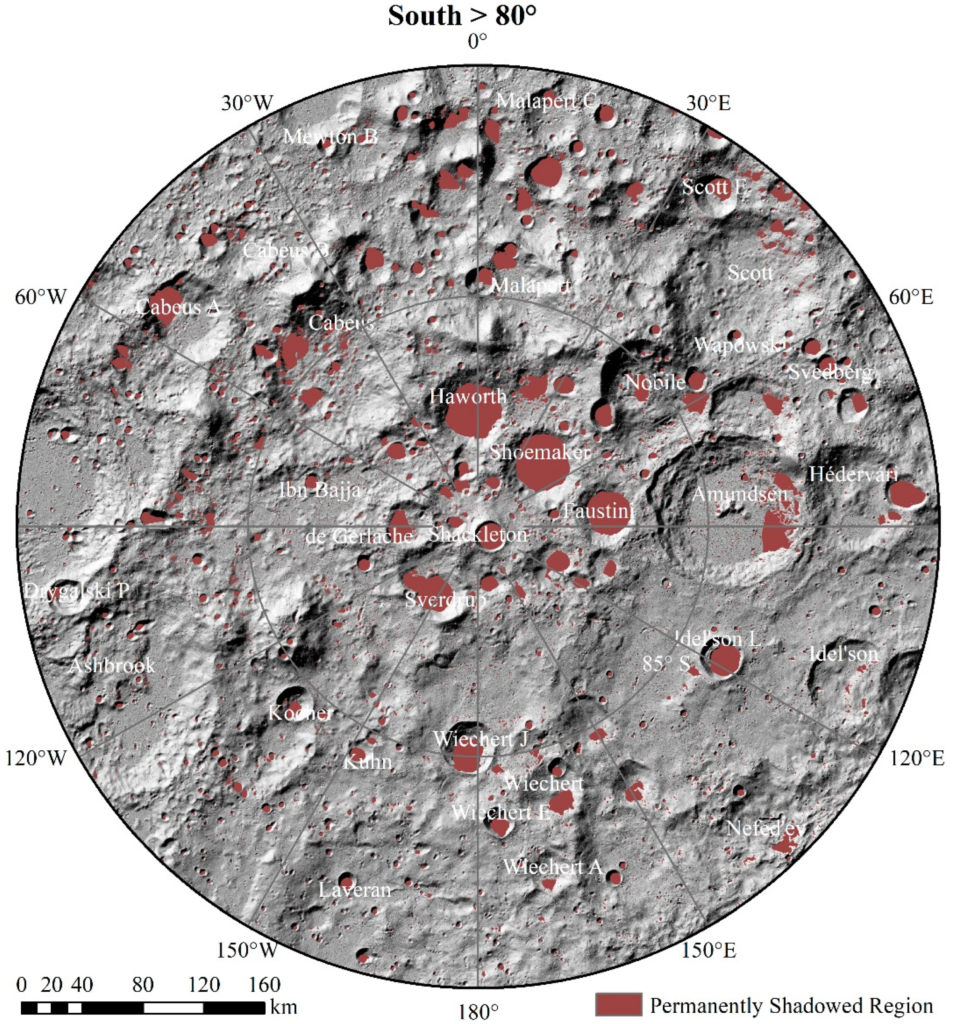
The South Pole
One such intriguing region is the lunar South Pole. Unlike other parts of the Moon, the South Pole holds strategic importance for several reasons:
- Water Ice Deposits: Recent missions have indicated the presence of water ice in permanently shadowed craters. This water is not just crucial for supporting future human missions but can also be broken down into hydrogen and oxygen. Potentially providing fuel for rockets and enabling longer space voyages.
- Constant Sunlight: Certain areas of the South Pole receive near-constant sunlight, offering a consistent source of solar energy. This makes it an ideal location for setting up solar-powered habitats and equipment.
- Scientific Potential: The South Pole’s unique environment, with its mix of light and shadow. Offers a treasure trove of scientific opportunities. Studying this region can provide insights into the Moon’s history. Its interaction with the solar wind, and possibly even clues about the early solar system.
Complementing the focus on the lunar South Pole is the development of the Gateway lunar command module. Envisioned as a space station orbiting the Moon, the Gateway is more than just a waypoint. It’s a hub of scientific activity, a staging point for lunar landings, and a platform for launching deep space missions, including those to Mars.
The Gateway
- Sustainable Lunar Exploration. Acting as a relay between Earth and the Moon’s surface, the Gateway will support regular crewed missions. Allowing for extended exploration and research on the lunar surface.
- Deep Space Readiness. By providing facilities for assembling, equipping, and launching long-duration missions, the Gateway will be instrumental in preparing for voyages to more distant destinations. Including asteroids and Mars.
- International Collaboration. The Gateway, with its modular design, offers opportunities for international partners to contribute modules, technologies, and expertise. Reinforcing the collaborative spirit of space exploration.
As we gaze into the future of space exploration, the Moon stands as a beacon, not as an end goal, but as a beginning. With its untapped resources, scientific potential, and the strategic importance of regions like the South Pole, coupled with infrastructures like the Gateway, the Moon is the stepping stone to our broader cosmic journey, leading us to destinations yet to be imagined.
Innovations in Aeronautics and Communication
The realm of space exploration is not just about rockets and rovers. It’s intrinsically linked to advancements in aeronautics and communication. As we venture deeper into space, the innovations in these fields play a pivotal role in ensuring our missions are efficient, sustainable, and connected.
Quiet Supersonic Transport
The dream of faster-than-sound travel has been around since the days of the Concorde. However, the sonic boom associated with supersonic flight has been a significant barrier, leading to restrictions over populated areas. Recent advancements aim to develop “quiet” supersonic aircraft, which can achieve high speeds without the disruptive sonic boom. These aircraft use innovative designs and materials to minimize shockwaves. Paving the way for faster international travel and potentially revolutionizing the aerospace industry.
Cleaner Aircraft Technologies
As concerns about environmental sustainability grow, the aerospace sector is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. Newer aircraft are being designed with fuel efficiency in mind, utilizing lightweight materials and aerodynamic designs. Additionally, there’s a push towards hybrid-electric propulsion systems and biofuels, aiming to make air travel more eco-friendly. These cleaner technologies not only benefit our planet but also represent a shift in thinking. Emphasizing sustainability even as we reach for the stars.
NASA
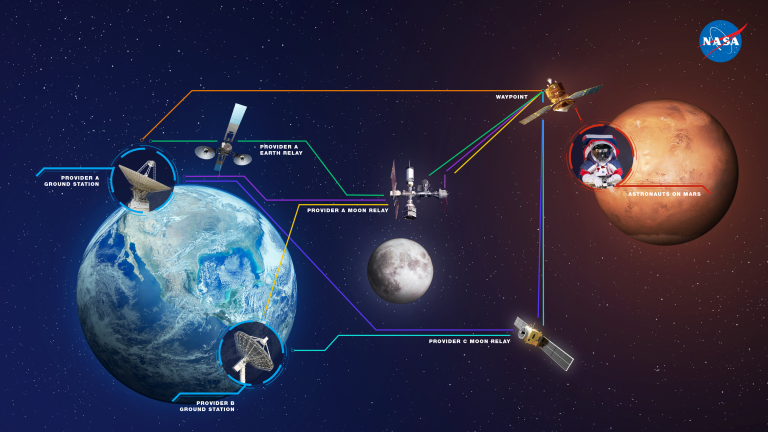
Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking (DTN)
Space is vast, and as we send missions farther from Earth, traditional communication methods become less reliable. Delays, disruptions, and long transmission times can hinder mission operations. Enter DTN – a new protocol designed specifically for the challenges of space communication. Unlike traditional networking, which expects a continuous connection, DTN is built to handle interruptions. It stores data during disruptions and forwards it once the connection is re-established, ensuring that vital information is not lost in the vastness of space. As we look towards missions to distant planets, asteroids, or even interstellar voyages, DTN will be crucial in keeping us connected.
As we dream of distant worlds and interstellar journeys. It’s the innovations on our home planet – in aeronautics and communication – that provide the foundation. These advancements ensure that our reach, whether in the skies above or the depths of space, is always guided by efficiency, sustainability, and connectivity.
The Promise of New Technologies and Missions
The horizon of space exploration is ever-expanding, fueled by a blend of cutting-edge technologies and ambitious missions. As we stand on the threshold of a new era in our cosmic journey, several upcoming missions and innovations promise to redefine our understanding of the universe and our capabilities within it.
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
Often hailed as the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, the JWST is set to be a game-changer in the world of astronomy. With a primary mirror nearly three times the size of Hubble’s and advanced infrared capabilities, the JWST is designed to peer further into space than ever before. Its mission objectives range from studying the atmospheres of exoplanets to capturing the light from the first galaxies formed after the Big Bang.The JWST represents the pinnacle of space telescopes and promises to unlock new chapters in our cosmic story.
Parker Solar Probe
Venturing closer to the Sun than any spacecraft before it, the Parker Solar Probe aims to “touch” our star. By plunging into the Sun’s outer atmosphere, or corona, the probe seeks to answer longstanding mysteries about solar winds, solar flares, and the fundamental processes that drive our Sun. Its resilient heat shield and innovative cooling systems allow it to withstand temperatures exceeding 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit. Making it a testament to human engineering and curiosity.
3D Printing in Space
The potential of 3D printing is not limited to Earth. In space, where resupplying is challenging and costly, the ability to manufacture tools, spare parts, and even habitats on-demand is invaluable. NASA and other space agencies are exploring the use of 3D printing for various applications. From creating medical tools aboard the International Space Station to building lunar bases using lunar regolith. This technology promises to revolutionize how we approach long-duration space missions and colonization.
Advanced Robotics
As we venture into hostile environments, whether it’s the surface of Mars or the icy moons of Jupiter, robots will be our vanguard. Advanced robotics, equipped with AI-driven decision-making capabilities, are being developed to explore, mine, and even construct in space. These robots can work in tandem with human astronauts. Handle tasks in environments too dangerous for humans, or operate autonomously in distant locales, paving the way for a new era of exploration.
The confluence of new technologies and missions is propelling us into a future where the boundaries of exploration are continually redefined. With each technological leap and every ambitious mission, we inch closer to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos and solidifying our presence in the vast expanse of space.
Preparing for Human Habitation Beyond Earth
As we gaze into the vastness of space, the dream of establishing a human presence beyond our home planet beckons. The idea of humans living and thriving in space, once the realm of science fiction, is now within the realm of possibility. However, realizing this dream comes with a myriad of challenges. And addressing them is crucial for the success of long-term human habitation beyond Earth.
Challenges of Long-Term Space Habitation:
- Life Support Systems. In the closed environment of a space habitat, ensuring a continuous supply of clean air, potable water, and nutritious food is paramount. Traditional resupply missions from Earth may not always be feasible, especially for distant colonies.
- Radiation Protection: Space is rife with harmful radiation, from solar flares to cosmic rays. Prolonged exposure can have detrimental effects on human health, necessitating robust shielding and protective measures.
- Psychological Well-being: Extended periods in the isolation of space can take a toll on mental health. The lack of natural environments, limited social interactions, and the vast distance from Earth can lead to feelings of isolation and stress.
- Gravity and Bone Density: In microgravity environments, like those on the International Space Station, astronauts experience bone density loss. For long-term habitation, addressing the effects of reduced gravity on the human body is crucial.
Solutions and Visions for the Future:
- Regenerative Life Support Systems: NASA and other space agencies are working on closed-loop systems that recycle air, water, and waste. Hydroponics and aquaponics are being explored for sustainable food production in space.
- Innovative Shielding: Research is underway to develop materials and technologies that can effectively shield habitats from radiation. This includes using local resources, like lunar or Martian regolith, to build protective barriers.
- Virtual Reality and Connectivity. To combat feelings of isolation, virtual reality and advanced communication systems can provide astronauts with immersive experiences. Connecting them to loved ones and recreations of natural Earth environments.
- Artificial Gravity. Rotating space habitats and centrifuges are being considered to create artificial gravity, helping mitigate the health effects of prolonged weightlessness.
NASA’s Vision for the Future:
NASA envisions a phased approach to human habitation beyond Earth. The Moon, with its proximity, serves as an ideal testing ground. The Artemis program aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Providing invaluable insights and technologies for future Mars missions. As for Mars, NASA’s goals are clear: send humans to the red planet, establish a permanent base, and lay the groundwork for a thriving Martian colony.
The journey to establish human habitats beyond Earth is filled with challenges, but with innovation, collaboration, and determination, a future where humans live among the stars is not just a dream, but a destiny waiting to be realized.
Conclusion
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in space exploration, it’s impossible not to be awed by the vastness of the universe and the limitless possibilities it holds. From the shimmering rings of Saturn to the distant galaxies that twinkle in the night sky, every corner of space beckons with mysteries waiting to be unraveled.
The journey thus far has been a testament to human ingenuity, resilience, and the insatiable thirst for knowledge. Each mission, whether it’s landing a rover on Mars or capturing the image of a black hole, is a step forward in our cosmic odyssey, a step closer to understanding our place in the grand tapestry of the universe.
But the road ahead is not one we tread alone. The future of space exploration hinges on continuous innovation, on pushing the boundaries of what’s technologically possible. It relies on collaboration, on the collective efforts of nations, organizations, and individuals coming together with a shared vision. And at the heart of it all is curiosity, that innate human trait that drives us to explore, to seek, and to discover.
As we look to the future, let us remember that space exploration is more than just rockets and rovers; it’s a reflection of who we are as a species. It’s our quest for knowledge, our ambition to reach beyond the known, and our hope to find our place in the cosmos. And as we continue this journey, let us carry forth with the spirit of discovery, for the universe is vast, and our exploration of it has only just begun.
FAQ
Q: Why is space exploration important?
A: Space exploration broadens our understanding of the universe, advances technology, fosters international collaboration, and has the potential to uncover answers to fundamental questions about our existence and the origins of life.
Q: How do astronauts survive in space?
A: Astronauts rely on life support systems aboard spacecraft and space stations. These systems provide essential needs such as oxygen, water, food, and protection from radiation and microgravity.
Q: What are the challenges of living on other planets?
A: Living on other planets presents challenges including extreme temperatures, radiation, lack of breathable atmosphere, and reduced or increased gravity. Solutions involve advanced habitats, protective gear, and sustainable life support systems.
Q: How is space exploration funded?
A: Space exploration is primarily funded by government space agencies like NASA, ESA, and Roscosmos. However, private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are playing an increasing role, funded by commercial ventures and partnerships.
Q: Are there plans for humans to colonize other planets?
A: Yes, there are visions and plans, especially for Mars. Organizations like NASA and private entities like SpaceX aim to send humans to Mars, with the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable colony.
Q: How do spacecraft communicate with Earth?
A: Spacecraft communicate with Earth using radio waves. Deep space missions rely on networks like NASA’s Deep Space Network, which uses large antennas to send and receive data across vast distances.
Q: What is the role of robots in space exploration?
A: Robots, like rovers and probes, play a crucial role in exploring environments that might be too dangerous or distant for humans. They can gather data, take samples, and test technologies for future human missions.
